The Internet of Things concept is drawing an increasing level of interest from manufacturers for a number of reasons, most notably its application in machine-to-machine (M2M) connections. (Access “Manufacturing and The Internet of Things” article to learn more.)
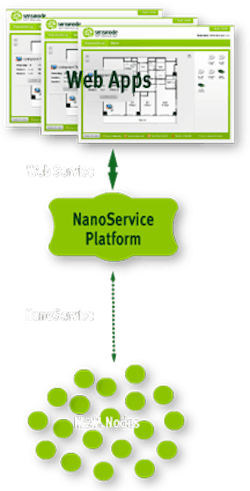
To help manufacturers implement an Internet of Things architecture and begin reaping the benefits of the increased manufacturing intelligence it can provide, Sensinode has released its NanoService platform for delivery and support of applications for the embedded Web. Sensinode is a developer of commercial 6LoWPAN and related IPv6 technologies for the embedded Internet.
The scalable NanoService platform is designed for deployment of M2M applications on private server, private cloud or public cloud environments. It provides a directory and semantic lookup of all deployed M2M nodes and resources in the system, provides transparent proxy services between the traditional Internet and constrained-resource protocols, and supports an eventing (asynchronous push) model.
Sensinode’s architecture for what it calls the Embedded Web includes device and Web application libraries for connecting devices and Web applications with the NanoService platform. The NanoService platform is essentially an application development environment for the creation of standard REST (Representational State Transfer) applications that conform to standards for embedded Web services such as CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol) and compact messaging protocols including EXI (Efficient XML Exchange). The NanoService platform is said to support low-power RF and cellular communication protocols including all variations of IEEE 802.15.4 RF at 2.4GHz and sub-GHz frequencies, as well as GSM cellular standards.
Reportedly able to support M2M networks of up to 20 million nodes and up to 100 million daily transactions per cluster, the NanoService platform can be applied for uses ranging from the Smart Grid to any number of industrial or consumer applications involving wireless sensing and control.
Currently, Sensinode is working with end-user organizations and M2M service provider companies on deployments of embedded Web applications using its NanoService platform. If you’re interested in working with Sensinode as it rolls out its NanoService platform, you can learn more at the www.nanoservice.com.
Sensinode
About the Author
David Greenfield, editor in chief
Editor in Chief
David Greenfield joined Automation World in June 2011. Bringing a wealth of industry knowledge and media experience to his position, David’s contributions can be found in AW’s print and online editions and custom projects. Earlier in his career, David was Editorial Director of Design News at UBM Electronics, and prior to joining UBM, he was Editorial Director of Control Engineering at Reed Business Information, where he also worked on Manufacturing Business Technology as Publisher.
Sign up for our eNewsletters
Get the latest news and updates