How to Select Antennas for Industrial Wireless Applications
Trust in wireless communications has spread rapidly across industry over the past several years. Once reserved primarily to connect equipment in places that were difficult to reach with wires or for rotating equipment unfriendly to additional wiring, wireless networking has now spread even in easy-to-wire applications because of its proven reliability and ease of setup and adaptability. Plus, we’ve all become much more comfortable with wireless through our nearly continuous reliance on smartphones.
To ensure the levels of reliability required by industry, attention to detail in wireless communication installation is more involved than setting up a home or office wireless network. To address the key issues around wireless antenna selection and setup for industrial applications, ProSoft Technology has released an educational video (which can be viewed at the bottom of this article) that explains many of the key facets of antenna technology that are quickly becoming a core requirement for industrial communications.
For example, the video highlights the differences in omni and directional antennas. To detail the antennas’ different types of signal sending and receiving capabilities as well as their range constraints, the video provides both verbal and graphic depictions.
The most common industrial types of wireless antennas are also discussed, including:
- Collinear array antennas (omni type) — which are essentially several linear antennas stacked on top of each other to increase gain to help receive/send signals from multiple directions;
- Width antennas (straight and articulating omni types) — widely used for mobile worker applications;
- Yagi (directional type)— composed of an array of linear elements so that the signal radiates in a beam from the antenna boom;
- Parabolic reflector (directional type) —a dish and feed antenna where power radiates from the feed antenna toward a reflector which concentrates the signal into a narrow beam; and
- Panel (directional type) — also known as a path antenna, these thin and rectangular antennas have a low profile and are weather resistant, but are not as focused as Yagi and parabolic types.
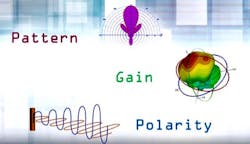
Three key electrical characteristics that affect antenna selection and placement—pattern, gain and polarity—are also spotlighted.
MIMO (multiple input/multiple output) is addressed in the video, explaining how this method takes advantage of a natural radio wave phenomenon known as multipath—where signals bounce off walls, ceilings and other objects to reach the antenna from multiple angles, multiple times. Though this radio wave behavior was known to cause signal interference in the past, MIMO-enabled antennas can take advantage of this multi-path behavior to increase communication performance. In fact, all wireless products with 802.11n support MIMO, which is key to allowing those devices to deliver much higher communication speeds.
Finally, the video address key antenna installation concerns, including frequency and polarity considerations, mounting location issues, hazard concerns, and how to assess gain requirements.