Vibe Coding: How Natural Language Programming is Changing Manufacturing Software Development
Why this article is worth reading:
- Vibe coding allows manufacturing personnel to create software using everyday speech instead of traditional programming, enabling production managers to simply say "build a monitoring dashboard for machine temperatures" and receive functional code.
- These programs can be used to address critical industry needs including equipment failure prediction, vision-based quality inspection systems, automated inventory management and rapid dashboard creation without requiring extensive programming expertise.
- While vibe coding accelerates development, AI-generated code requires expert review for security vulnerabilities and regulatory compliance, especially FDA 21 CFR Part 11, to ensure solutions meet operational safety standards before deployment.
The development of vibe coding represents a vital breakthrough with artificial intelligence through its ability to convert ordinary descriptions into functional code. This ability is poised to transform the software development process while enabling manufacturing companies to leverage more AI capabilities.
What is vibe coding?
The term "vibe coding" was coined by computer scientist Andrej Karpathy, co-founder of OpenAI, in 2025 to describe an AI-based development process that turns human instructions into code using natural language inputs. Traditional coding methods require manual line-by-line programming, but vibe coding lets users define their goals and solve problems creatively while the AI system implements the technical details.
This method is built on large language models and AI tools including ChatGPT, GitHub Copilot, Replit and Cursor. The platforms operate to understand user commands while offering code recommendations along with real-time task automation and issue resolution capabilities. Vibe coding also extends into agentic AI when those assistants are empowered to take multi-step actions autonomously. In effect, vibe coding encompasses both LLMs and agentic AI, with an emphasis on the shift from rigid programming to natural language-driven, goal-oriented workflows.
Why vibe coding matters for manufacturers
The manufacturing industry depends on AI for predictive maintenance, quality control, supply chain optimization and robotics operations. The typical process of building and implementing AI-based solutions demands substantial programming expertise and extensive time from developers. The implementation of vibe coding creates a system which allows production engineers, operational staff and even non-technical personnel to express their needs using everyday speech for the AI to produce the necessary software components.
AI-generated code used in systems subject to FDA 21 CFR Part 11 regulations must be thoroughly validated, documented and audited, including maintaining audit trails, ensuring data integrity and implementing proper access controls.
The implementation of vibe coding creates a system which allows production engineers, operational staff and even non-technical personnel to express their needs using everyday speech for the AI to produce the necessary software components.
For example, a production manager can instruct an AI assistant with the following command: “Build a monitoring dashboard to check machine temperatures while alerting when any measurement exceeds 80°C.” The AI system would automatically produce the required programming code which allows users to deploy new solutions quickly because developer resources are not limited by a lack of time.
Real-world vibe coding applications
Some of the most immediate applications for vibe coding in the manufacturing industries include:
- Equipment failure prediction through sensor data analysis. Maintenance personnel can use plain language descriptions through vibe coding to trigger the AI system, which then produces code for data collection, analysis and visualization.
- Vision-based inspection systems — using the command "detect surface defects on product X using camera feeds," engineers can ask the AI system to create and improve the required programming code.
- Automatic management of inventory tracking alongside demand forecasting and logistics operations. With user-defined criteria, AI can combine multiple data sources to produce dashboards and alerts.
- Create intuitive dashboards and control panels at high speed with little or no programming expertise required.
The implementation of vibe coding creates a system which allows production engineers, operational staff and even non-technical personnel to express their needs using everyday speech for the AI to produce the necessary software components.
The vibe coding workflow
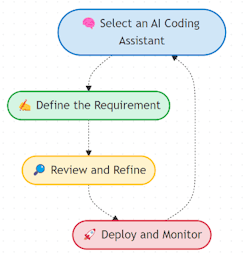
Following is the workflow process using vibe coding to create a program:
1. Select an AI coding assistant: Choose a platform such as Replit, GitHub Copilot or Cursor based on technical needs and integration requirements.
2. Define the requirements: Clearly state the desired outcome in plain language. The specificity and clarity of the prompt directly influence the quality of the AI-generated code.
3. Review and refine: The AI produces initial code, which is then reviewed and refined by human experts. This iterative process ensures that the software meets operational and safety standards.
4. Deploy and monitor: After final review, the code is deployed in the production environment. Continuous monitoring and feedback help further optimize the solution.
Point 3 above is critical. While vibe coding for common tasks tends to be highly reliable, you should always have programming experts review the code before implementation.
Vibe coding challenges and considerations
While vibe coding offers significant advantages, it is not without challenges. The most critical ones are:
- Code quality and security: AI-generated code may contain vulnerabilities or inefficiencies. Studies show that AI-generated code snippets have security flaws, underscoring the need for human oversight and rigorous testing.
- Complexity limitations: Vibe coding excels at standard tasks but may struggle with highly specialized or novel technical challenges that require deep domain expertise.
- Dependence on training data: The quality and relevance of AI-generated code depend on the data used to train the underlying models. Outdated or biased data can lead to suboptimal solutions.
- Human oversight required: True creativity, goal alignment and critical thinking remain the domain of human experts. Vibe coding should be seen as a collaborative tool, not a replacement for skilled engineers.
- Regulatory compliance: For industries such as pharmaceuticals and medical devices, where software development must adhere to strict regulatory standards, vibe coding introduces additional challenges. FDA 21 CFR Part 11 establishes requirements for electronic records and electronic signatures to ensure their trustworthiness, reliability and equivalence to paper records. AI-generated code used in systems subject to these regulations must be thoroughly validated, documented and audited to comply with Part 11 requirements, including maintaining audit trails, ensuring data integrity and implementing proper access controls. Failure to meet these standards could result in non-compliance issues, making human oversight and robust validation processes even more critical in regulated environments.
The future of vibe coding in manufacturing
Vibe coding is still in its early stages, but its impact on manufacturing is already evident. As AI models become more sophisticated and multimodal — incorporating voice, text and visual inputs — the potential for intuitive, rapid and collaborative software development will only grow. Manufacturers that embrace this approach will be well-positioned to lead in the era of smart factories and Industry 4.0.
Nikhil Makhija is a member of MESA International and an SAP Manufacturing Suite expert with more than 16 years of specialized experience in optimizing manufacturing processes with SAP solutions.
More AI in manufacturing content from Automation World:
About the Author

Nikhil Makhija
Nikhil Makhija is a MESA member and independent industry researcher.